| Sign In | Join Free | My carsrow.com |
|
- Home
- Products
- About Us
- Quality Control
- Contact Us
- Get Quotations
| Sign In | Join Free | My carsrow.com |
|
Brand Name : DINGSCO
Model Number : According to customers requirements
Certification : ISO 9001:2015,PED 2014/68/EU,API 6A,API-20B,TSG,NORSOK
Place of Origin : China
MOQ : Negotiable
Price : Negotiable
Payment Terms : T/T
Supply Ability : Negotiable
Delivery Time : (Sample Order) 7 days
Packaging Details : According to Customers' Requests
Product Name : Nickle Alloy Sheets
Grade : Inconel 600
Density : 8.47 Mg/m³
Specific Heat : 0.106Btu/lb-°F
Permeability at 200 oersted (15.9 kA/m) : 1.010
Electrical Resistivity : 620ohm-circ mil/ft
UNS : UNS N06600
Curie Temperature : -124°C
Nickle Alloy Sheets Inconel 600 Petrochemical Industry Nuclear Thin Medium
Nickle Alloy Sheets: Nickel alloys sheets are alloys composed of nickel as the base metal with other elements added. The Monel alloy, which contains about 30% copper, developed around 1905, was one of the earlier nickel alloys. Nickel possesses excellent mechanical, physical, and chemical properties, and the addition of suitable elements can enhance its oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and improve certain physical properties.
Classification:
Applications:
Development History:
INCONEL ALLOY 600 (nickel-chromium-iron)(UNS N06600/W.Nr. 2.4816) is a standard engineering material for applications which require resistance to corrosion and heat. The alloy also has excellent mechanical properties and presents the desirable combination of high strength and good workability.
Characteristics:
The excellent mechanical properties of this alloy endow the material with high strength and good workability. It has good corrosion resistance, especially in alkaline environments, and can be used in low and high temperature environments.
Corrosion Resistance:
Alloy 600 is able to withstand a variety of corrosion. The alloy has excellent resistance to alkaline solution performance and good resistance to strong oxidizing acid solution performance. It is particularly resistant to the erosion of dry chlorine or hydrogen chloride even at temperatures up to 650°C.
Typical Applications:
Recommended Tool Types & Machining Conditions:
| Operations | Carbide Tools |
| Roughing, with severeinterruption | Turning or Facing C-2 andC-3 grade: Negative rakesquare insert, 45° SCEA1,1/32 in. nose radius. Tooholder: 5° neg. back rake5° neg. side rake. Speed:30-50 sfm,0.004-0.008 in.feed, 0.150 in depth of cut.Dry2, oil3, or water-base coolant 4. |
| Normal roughing | Turning or Facing C-2 orC-3 grade: Negative ratesquare insert, 45° SCEA,1/32 in nose radius. Tooholder: 5° neg. back rake5° neg. side rake. Speed:90 sfm depending on rigidity of set up, 0.010 infeed, 0.150 in. depth ofcut. Dry, oil, or water-base coolant. |
| Finishing | Turning or Facing C-2 0rC-3 grade: Positive rakesquare insert, if possible45° SCEA, 1/32 in.noseradius. Tool holder: 5° pos.back rake, 5° pos. siderake.Speed: 95-110 sfm0.005-0.007 in. feed,0.040 in. depth of cut. Dryor water-base coolant. |
| Rough Boring | C-2 or C-3 grade: lf inserttype boring bar, use standard positive raketools with largest possibleSCEA and 1/16 in. nose radius. lf brazed tool bargrind 0° back rake, 10° posside rake, 1/32 in. nose radius and largest possible SCEA.Speed: 70 sfm depending on the rigidityof setup, 0.005-0.008 infeed, 1/8 in. depth of cut.Dry, oil or water-base coolant. |
| Finish Boring | C-2 or C-3 grade: Usestandard positive raketools on insert type bars.Grind brazed tools as fofinish turning and facingexcept back rake may bebest at 0°. Speed: 95-110sfm,0.002-0.004 in feed.Water-base coolant. |
Thermal Properties:
| Temperature | Coefficient of Expansiona | Electrical Resistivity | Thermal Conductivity | Specific Heat |
| °F | 10-6 in/in•°F | ohm•circ•mil/ft | Btu•in/ft2•h•°F | Btu/lb•°F |
| -250 | 6.0 | - | 86 | 0.073 |
| -200 | 6.3 | - | 89 | 0.079 |
| -100 | 6.7 | - | 93 | 0.090 |
| 70 | 5.8 | 620 | 103 | 0.106 |
| 200 | 7.4 | 625 | 109 | 0.111 |
| 400 | 7.7 | 634 | 121 | 0.116 |
| 600 | 7.9 | 644 | 133 | 0.121 |
| 800 | 8.1 | 644 | 145 | 0.126 |
| 1000 | 8.4 | 680 | 158 | 0.132 |
| 1200 | 8.6 | 680 | 172 | 0.140 |
| 1400 | 8.9 | 680 | 186 | 0.145 |
| 1600 | 9.1 | 686 | 200 | 0.149 |
| 1800 | 9.3 | 698 | - | - |
| 2000 | - | 704 | - | - |
| °C | μm/m•°C | μΩ•m | W/m•°C | J/kg•°C |
| -150 | 10.9 | - | 12.5 | 310 |
| -100 | 11.7 | - | 13.1 | 352 |
| -50 | 12.3 | - | 13.6 | 394 |
| 20 | 10.4 | 1.03 | 14.9 | 444 |
| 100 | 13.3 | 1.04 | 15.9 | 444 |
| 200 | 13.8 | 1.05 | 17.3 | 486 |
| 300 | 14.2 | 1.07 | 19.0 | 502 |
| 400 | 14.5 | 1.09 | 20.5 | 519 |
| 500 | 14.9 | 1.12 | 22.1 | 536 |
| 600 | 15.3 | 1.13 | 22.1 | 578 |
| 700 | 15.8 | 1.13 | 25.7 | 595 |
| 800 | 16.1 | 1.13 | 27.5 | 611 |
| 900 | 16.4 | 1.15 | - | 628 |
Physical Properties & Mechanical Properties:
| Physical Properties | |||
| Mean Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | |||
| Temperature Range | |||
| °F | °C | in/in°F | cm/cm°C |
| 68 | 20 | 5.8 x 10-6 | 10.4 x 10-6 |
| Mechanical Properties | |||
| Typical Values at 68°F(20°C) | |||
| Yield Strength 0.2% offset psi | Ultimate Tensile Strength (min.) psi | Elongation in 2"% | |
| 35,000 | 80,000 | 30 | |
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Ni+Co | Cr | Fe | C | Mn | S | Si | Cu |
| Minimum(%) | 72 | 14 | 6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Max(%) | - | 17 | 10 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.015 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
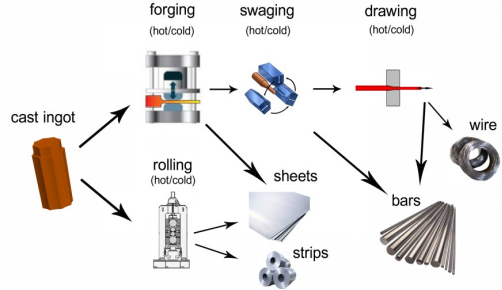
Processing Flow Chart:

|
|
Thin Medium Nickel Alloy Sheets Inconel 600 Plates for Petrochemical Industry Images |